With its strong influence on the multilateral trading system, the US is undoubtedly amongst the most powerful countries in the world when it comes to trade. Over the course of his presidency, Trump’s “America First” policy, however, has increasingly been undermining international trade laws. Over the past few years, the US president has been fighting numerous battles with some of America’s trading partners, using tariffs for leverage in negotiations. And although it may look like he’s done a lot, has this led to any progress? Let’s take a look at the main measures that Mr Trump has taken to protect American trade over the past four years.
The US vs. China trade war
The trade war with China which President Trump announced in 2018 is the most prominent trade conflict we’ve witnessed in recent years. The US President has been accusing China of unfair trading practices and intellectual property theft for years, whilst China has long believed that the US is attempting to curb its rise as an economic powerhouse.
The dispute has seen the two countries impose tariffs on hundreds of billions of dollars worth of one another's goods and although they recently signed a preliminary deal[1], some of the most complex issues remain unresolved and most of the tariffs are still in place. The US will maintain levies of up to 25% of approximately $360bn worth of Chinese products, whilst China is anticipated to keep tariffs on over $100bn of US goods.

United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA)
Back in 2018, the US, Canada and Mexico signed a successor to The North American Free Trade Agreement (Nafta) which was renamed as the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement or USMCA. The agreement governs over $1.1 trillion worth of trade between the three North American countries.
Renegotiating Nafta was one of Trump’s key goals for his presidency. "The terrible NAFTA will soon be gone. The USMCA will be fantastic for all!", he tweeted shortly after signing the new deal with America’s neighbouring countries.
However, despite the name change and the claims that the updated agreement would "change the trade landscape forever", a lot of the terms have remained the same[2]. Stronger labour provisions and tougher rules on the sourcing of auto parts were some of the most notable changes, however, analysts believe that their significance remains to be seen.
What’s more, a number of the other updates were discussed during negotiations which took place before Trump took office.
Tariffs on European cheese, wine & aircraft
There hasn’t been a trade deal agreed with the Europan Union as of yet. In 2018, after the US introduced tariffs of 25% on steel and 10% on aluminium imported into the country, the two sides went through a round of tit-for-tat tariffs with the EU announcing retaliatory tariffs on US goods such as bourbon whiskey, motorcycles and orange juice. A few months later, in October, the US imposed a new round of tariffs[3] on $7.5bn of EU goods, including French wine, Italian cheese and Scotch whisky. The US also imposed a 10% levy on EU-made airplanes which could hurt US airlines that have ordered billions of dollars of Airbus aircraft.
President Donald Trump has also repeatedly threatened to impose additional tariffs on European cars and although that hasn’t materialised yet, he has confirmed that he’s serious about it when he recently mentioned his plans again[4] during the World Economic Forum in Davos.
Trade deals with South Korea & Japan
One of Trump’s first moves as President of the US was to withdraw the country from the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) – a proposed trade agreement between 12 countries, which eventually went ahead without America. Since then, Mr Trump has claimed two bilateral agreements with South Korea[5] and Japan[6]. However, the changes were so limited that Congressional researchers concluded that they barely qualified as trade deals.
With Japan, the US agreed on either levy cuts or full elimination on $7bn worth of agricultural goods, which is what it would have received under the Trans-Pacific Partnership too.
The most notable win that came from the agreement with South Korea is the extension of the 25% US tariffs against South Korean light-duty trucks to 2041. Previously, it was scheduled to expire in 2021.
Tariffs on steel and aluminium from Brazil and Argentina
In December last year, Mr Trump surprisingly announced on Twitter that he’s ‘restoring’ tariffs on steel and aluminium imports from Brazil and Argentina.
The two South American nations have been exempted from higher duty on both metals, but according to President Trump, both countries had been devaluating their currencies which he believes is ‘not good’ for American farmers.
There hasn’t been much progress since the initial announcement, but Brazil’s President Jair Bolsonaro said he had been assured by Trump that the tariffs won’t materialise.
[1] https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/business-51114425
[2] https://markets.businessinsider.com/news/stocks/us-canada-mexico-trade-deal-usmca-nafta-details-dairy-auto-dispute-resolution-2018-10-1027579947
[3] https://www.independent.co.uk/news/business/news/us-tariffs-trump-eu-goods-airbus-subsidies-wto-a9132001.html
[4] https://www.marketwatch.com/story/trump-doubles-down-on-threats-to-impose-tariffs-on-european-cars-at-davos-2020-01-21
[5] https://www.cnbc.com/2018/09/24/trump-signs-revised-trade-deal-with-south-korea.html
[6]https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/business-49834705
The company’s report, ‘Saudi Aramco After IPO – Company Overview and Development Outlook’, reveals that five major expansion projects – four crude and one natural gas – are being planned to boost output in the country.
One eighth of the world’s crude oil from 2016 to 2018 was produced by Saudi Aramco. As well as being the world’s largest oil producing company, it is also the most reliant on oil production, with 88% of its total 2018 upstream production coming from crude.
Somayeh Davodi, Oil and Gas Analyst at GlobalData, commented: “The major expansions at Saudi Aramco’s offshore oil fields of Marjan, Zuluf, Safaniyah and Berri are expected to comprise the majority of the company’s upstream investment over the next three years. Although these developments will also add gas and NGL capacity, the main addition will be oil.”
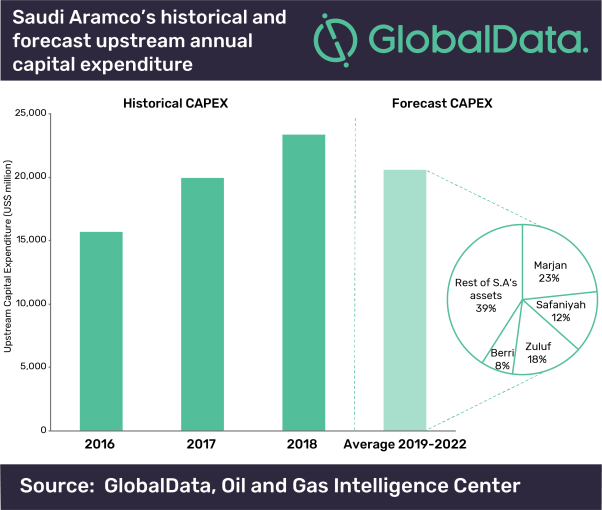
In 2018, the company’s MSC capacity (maximum barrels of crude oil that can be produced during a year) was 12 million barrels per day (bd) with 10.5 million bd oil produced plus the remaining 1.5 million bd available as spare capacity. This capacity allows flexibility to respond to market supply and demand fluctuations. The new expansions will add 1.45 million bd additional oil capacity.
Davodi adds: “Future production, including the ability to realize output gains from new capacity additions, is likely to be highly dependent on OPEC quotas. Production cuts are set to continue into 2020, but could be extended further.”
Bankruptcy is a legal process that relieves you off your debt for some time, but in the long run, declaring bankruptcy can have a very serious effect on your credit report and remains for almost 7-10 years on your report affecting your ability to get loans in the future. So, I am going to present you with four alternatives that can save you from bankruptcy. Going for one or all of these options is definitely better than going bankrupt.
1. Enter an IVA Program
An IVA is an individual voluntary agreement that is a legal binding contract between you and those you owe money. After you have signed an IVA, you get a period of time, usually 5 years, during which you can pay off the debt you owe. It prevents all the creditors from taking any action against you. The best thing about an IVA is that you get to keep your home and personal items. Over the past few years, IVA’s have become a lot more popular. If you want IVA help and information, head over the link and learn more about it.
2. Sell Some Assets
Paying off debt should be your foremost priority. Sell whatever you have in excess and whatever you can live without. If you notice that you can’t keep up with your payments, immediately take action. Many people think that they can’t live without luxurious things, but in the long run, you will understand that it is only temporary and things will get better.
[ymal]
3. Talk With Your Credits
Now I know this sounds crazy, but hear me out. Most creditors would rather get some money from you than getting none at all. Bankruptcy affects your creditors as much as it affects you. If you talk with your creditors before filing for bankruptcy and let them know that you are having financial difficulties they might listen. Most creditors have special hardship programs to assists you in your time of need. Ask them if they can lower the amount of monthly payments or lower your interest rate. Believe it or not, you can sweet talk you way out of bankruptcy.
4. Get Help from Friend and Friendly
Borrowing money from friends and family is a very bad idea, and it should be your last resort. Money has the power to create misunderstanding between lifelong friends, so you should be very careful. Calculate how much money you need and how much money can you pay off on your own. Never take more than what you need and pay up as soon as you can. Most importantly, before asking them for money, you should have a clear plan on how you are going to pay them back. Your family and friends will happily help you but don’t take advantage of their kindness and earn their trust for the future by paying them what you owe without them asking for it.
In particular, limited-edition trainers have a huge appeal across the world, with people willing to camp outside of stores to pick up a particularly lucrative pair.
This highlights that despite the stereotype of the younger generation being frivolous with their money, it seems they are actually one of the savviest generations when it comes to turning a profit on their own. While they are hesitant to invest in stocks, millennials and generation Z are tapping into the hyper-short-term investment of fashion and beauty.
1. Clothes
Although the initial purchase is an investment, with many resellers spending hundreds of pounds or more on such a venture, but the resale of these goods can certainly turn a profit. It also taps effectively into the Instagram world we’re living in too. Sellers often combine their shop platforms with their social media accounts to merge both modelling and selling the items.
There are so many stories about how entrepreneurial millennials are sniffing out limited edition items from the most popular brands, such as Supreme, during their famous limited edition ‘drops’, then rapidly reselling them. Perhaps one of the reasons why the younger generations are turning more to side-hustles and reselling as forms of investment is that the turnover is incredibly fast thanks to apps like Depop.
2. Shoes
Arguably the biggest market in reselling is that of sneakers and trainers. Much like clothing, the main draw here is in limited edition shoes — but the sneakerhead culture is not anything new. In fact, it began nearly 30 years ago, though it’s enjoyed a huge resurgence in the last few years.
The most sought-after trainers tend to be either limited edition silver trainers or classic men’s white trainers for that much-loved vintage style. People are willing to set up camp outside a store before a particularly hyped drop of limited-edition trainers, in order to grab them at retail price, then sell it on for much higher prices.
Some might seek to resell the items quickly, but there’s certainly a case to be made for popping a brand new pair of limited edition trainers away for a few years before reselling in hopes that their much-hyped status will only increase that price tag as the years roll on.
3. Art flipping
According to Business Insider, rich millennials are snapping up art as financial assets rather than as part of a potential collection — 85 per cent of millennials purchasing artworks say they are aiming to sell in the next year.
Buying art with the intention of selling it on quickly is known as art flipping, and it’s something of a controversial subject in the art world. However, there are some who consider the process of art flipping as a potentially devaluing practice that harms the artist and their work highlighting that this investment isn’t perhaps for everyone.
The process can also seem more logical than artistic too, as many such purchases are made purely on the work’s monetary value. But, just like with clothing and trainers, the piece’s social media hype can also spur rich millennials to part with their cash in a hopes of a quick resale profit — Instagram has been highlighted by Adweek as a viable platform for creating social media adoration for artists.
Sources: https://www.sofi.com/blog/millennial-investing-trends/ https://www.adweek.com/digital/influencing-the-art-market-millennial-collectors-social-media-and-ecommerce/ https://www.businessinsider.com/rich-millennials-investing-art-flipping-build-wealth-2019-4?r=US&IR=T https://www.standard.co.uk/fashion/should-you-be-investing-in-sneakers-a4014486.html https://www.theguardian.com/fashion/2017/oct/23/teens-selling-online-depop-ebay
That possibility has pushed many government bond yields to new lows in recent weeks, while global equity prices have been volatile. Below Rhys Herbert, Senior Economist, Lloyds Bank Commercial Banking looks at the evidence.
And while some economic data might be confusing, I think there is a clear message.
First, that global economic growth has slowed and may slow further, and second, that there is a pronounced difference between weak or even falling activity in the manufacturing sector and still relatively buoyant service sector.
So, what might be causing this?
Manufacturing v services
It seems probable that the manufacturing sector is being hurt by the ongoing trade dispute between the US and China. Indeed, the US manufacturing sector is now in decline for the first time in a decade.
And the Bank of England (BOE) flagged last week that, because the trade war between the US and China had intensified over the summer, the outlook for global growth has weakened.
The Bank’s Monetary Policy Committee added that the trade war was having a material negative impact on global business investment too.
The main impact is on confidence - or more accurately lack of confidence – which is holding manufacturers back from investing. As a result, we’ve seen a slowdown in world trade and in demand for manufactured goods.
In contrast, demand for services is being supported by relatively buoyant consumer spending. Yes, consumers are probably reluctant to splash out on big ticket items like cars right now, but overall, they are still willing to spend.
Consumers are probably reluctant to splash out on big ticket items like cars right now, but overall, they are still willing to spend.
The central conundrum
The key question going forward is whether it is more likely that manufacturing rebounds or that service weaken from here?
That is the conundrum that central banks need to weigh up in setting policy.
So far, the majority have decided that they are sufficiently concerned about the downside risks to take out some insurance and adopt policies designed to support economic growth.
Back in July, the US Federal Reserve did something it had not done for over a decade. It reduced interest rates – by a quarter point to 2.25% (upper bound).
It was widely seen as an insurance move against increasing global economic headwinds, emanating mainly from the US-China trade dispute.
[ymal]
It repeated the move last month, lowering the target range for its key interest rate by 25 points to between 1.75% and 2%. The accompanying statement repeated July’s message that, while economic conditions are probably sound, a bit of insurance against downside risk was advisable.
Meanwhile, in his penultimate meeting in September, this month, European Central Bank President Mario Draghi announced a package of stimulus measures including a reduction in its deposit rate to a record low of -0.5% and the introduction of a two-tier system to exempt part of banks’ excess liquidity from negative rates.
He also announced a resumption of the bond-buying programme at €20bn a month from November and, importantly, signalled no end date to purchases.
Draghi can argue that the weak Eurozone PMI suggests the economy is stagnating, supporting this action.
But the UK has not followed this strategy.
On the sidelines
The BOE is still wary enough about potential inflationary pressures from a tight labour market and rising wage growth to talk about the possibility of interest rates needing to go up.
But last month, the BOE concluded that the longer that uncertainty goes on, the more likely it is that growth will slow, especially given the weak global economy.
We will see if the message changes, but the likelihood is that BOE rate setters will want to continue to remain on the sidelines and keep rates unchanged at 0.75%, not least because the Brexit outcome remains unsettled.
The government’s official preferred Brexit position is for a deal and that assumption in the Bank’s forecast points to interest rates rising “at a gradual pace and to a limited extent”.
But the BOE also noted growing concerns about risks to growth, joining the US Federal Reserve and the European Central Bank, which both seem to have decided that risks are skewed to the downside.
But, while escalating tariff wars, slowing growth in the US and China and Brexit uncertainty mean there are credible reasons to worry that 10 years of steady expansion could be coming to an end, it is still far from certain that the current slowdown means a recession is looming.
Celine Hartmanshenn, Global Head of Credit from Stenn Group, an international provider of trade finance, provides her thoughts on the deficit fall.
The trade gap between China and the US is shrinking, reflecting the overall softening of global trade volumes and hinting at the movement of supply chains out of China.
US macro indicators are mixed. Unemployment remains low and prices are in check. But consumer and business spending has cooled, manufacturing output is at its lowest level in a decade, and the services sector – which accounts for 80% of economic activity – is slowing down. The lingering uncertainty stemming from the trade war and sagging global economy has caused the outlook for 2020 to dim, with the expectation of the US limping along at 1-2% GDP growth. It’s not an outright recession, but it’s certainly not a boom either.
There’s no denying that the US-China trade war is a drag on the US economy. The disruption to supply chains is expensive for businesses, the tariffs now cover a wide range of goods, and because financial markets can’t quickly adjust, they are more volatile.
So, what’s the solution? Certainly not a tariff war with the EU. The US will implement its first tariffs on aircraft and agricultural goods in 2 weeks. The EU is likely to retaliate. The aftershocks could easily tip the US into recession.
The world will be watching this month as China and the US go back to the negotiating table. Whether they like it or not, these two economies are interconnected. China is dealing with massive overcapacity, high debt levels and a need for US dollars. And the US relies on China pumping these dollars back into the US to fund its debt.
The VIX volatility index – which is commonly used to gauge the fear level among investors – jumped by 36%, leading the markets to become particularly volatile. Losses have been widespread. In the week of the 5th of August alone, the NASDAQ plunged 3.5%, the S&P 500 and Dow Jones both dropped 3%, the FTSE 100 fell by 2.5% and both the French CAC 40 and German DAX 30 saw decreases of around 2%.
With neither side willing to be the first to blink, investors are increasingly seeking out ways to properly insulate themselves from the instability of the market. However, given the unpredictability of the conflict itself, this is no simple task. So, to help you make the best decisions that you can, here André Lavold, CEO of Skilling, takes a look at what has gone on and how some key stakeholders have reacted.
The present state of play: tariffs, tweets and devaluations
Under this current American administration, trade conflicts are never truly resolved; instead being defined by periods of escalation and détente. May saw the US choose to increase the levels of tariffs on $200 billion of Chinese goods, to which the Chinese responded by raising tariffs of its own on $60 billion of US goods. At the G20 summit in Osaka, both sides publicly agreed to a ‘truce’, however this was almost immediately reneged upon by the Americans after the President tweeted that he would levy an additional tariff of 10% on $300 billion of Chinese goods.
This brings us to the current state of play. While the US and China have always treated each other in an adversarial fashion, the latest measures have escalated the conflict to a new level of significance. The latest round of tariffs, most of which will be introduced in the autumn and winter of this year, now focus on consumer-facing goods like electronics and clothing. Companies with significant exposure to China – such as Nike and Apple, who saw their stock prices fall by 3% and 5.2% respectively – were especially affected. With importers likely to pass on the price rise to consumers, these new measures will likely negatively impact consumer spending. With the US household being the backbone of the American economy, the odds of a severe economic slowdown or recession are increased.
Companies with significant exposure to China – such as Nike and Apple, who saw their stock prices fall by 3% and 5.2% respectively – were especially affected.
Knowing that this was likely to hurt its export-reliant economy, the Chinese took action. The People’s Bank took the strategic decision to allow the Yuan to depreciate below the seven per dollar rate for the first time since 2008. Being a floor that the Chinese Government had vigorously defended in past, many have suggested that this was a retaliation against the latest round of tariffs. While it’s only possible to speculate on whether this was indeed retaliation, there would be scores of evidence to suggest so. The positive current account balance which China maintains with the US means that its own tariffs are not as effectual as those implemented by the United States. However, by letting the Yuan weaken, this not only reduces the price of Chinese exports but also reduces the profit of American companies with operations in China.
Spillover: has a trade war become a currency war?
Having considered China’s actions as combative, the United States took the historic decision of labelling China as a currency manipulator; the first time it had done so since the Clinton administration in 1994. The President has also previously attacked the Federal Reserve for not choosing to cut interest rates, stating that this has led to an appreciation in the value of the dollar; making American organisations uncompetitive on the global market.
His rhetoric, combined with the greater chances of a global economic slowdown, suggests that a devaluation in the dollar could be forthcoming. A tough business environment would vastly increase the likelihood of intervention – be it quantitative easing, or lower interest rates – and this would result in the dollar losing value.
With both sides now flirting with the idea of a currency ‘race to the bottom’, this could develop into a very dangerous game of chicken.
With both sides now flirting with the idea of a currency ‘race to the bottom’, this could develop into a very dangerous game of chicken. While China has much to gain from a devaluation, it also has much to lose. Let the currency slide too far, and there is a great risk of capital flight. Similarly, as previously mentioned, given that the US retains a trade deficit of approximately $488 billion, it will be hard to let the dollar fall without impacting its own businesses.
The ultimate effect of this will be volatility in the currency markets, especially in the USDCNY pair, and for traders, this can create lots of opportunities.
Wider reactions
With such unpredictable market forces at play, currencies and commodities that are considered ‘safe havens’ such as the Japanese Yen, the Swiss Franc and Gold have seen rises, as traders look for ways to protect their earnings. As long as the market remains volatile, they will continue to be good prospects. However, with the Japanese economy also being very reliant upon exports, traders should be wary of potential intervention.
The conflict has also led to lower oil prices, as doubts have been expressed in the general economic climate. This has impacted commodity currencies such as the Canadian Dollar and Norwegian Krona. The Australian Dollar has been doubly impacted as, in addition to being relatively reliant on natural resource exports, its economy is also uniquely exposed to the Chinese market.
Given the present impasse, it’s becoming increasingly likely that the trade war will not cease for some time. With both sides willing to dig their heels in, it may take a governmental change for the situation to develop any further. However, in the meantime, there are steps that you can take to protect your earnings. Minimise the risk of loss by auditing your portfolio and making sure that you’re comfortable with its allocation. By doing so, you ensure that you continue to earn at your fullest potential.
While some are interested in obtaining a bit of extra liquidity for personal use, others are motivated due to the fact that such funds can be used to become partnered with a trusted B2B ecommerce platform.
The main question involves whether or not virtual trading represents a sound fiscal strategy or an unnecessary risk. Let us take a look at this subject from a decidedly objective point of view in order to better appreciate the big picture.
Valid Promises or Smoke and Mirrors?
Countless virtual trading platforms claim that financial freedom is only moments away when using their utilities and tools. However, the fine print tells another story. It stresses the fact that online trading involves a fair share of risk and such a strategy should only be undertaken by those who are capable of absorbing substantial losses within a short period of time. The main question therefore involves whether or not both of these claims are justified.
The first main takeaway point is that each trader will have to define his or her own levels of acceptable risk. As opposed to trading for fun or as a side project, those who are looking to obtain extra liquidity for a business venture need to be very careful in regards to what strategies are adopted. In other words, is the ultimate risk worth the expected reward?
It should be mentioned that any online investment portal is only as useful and lucrative as the experience of the trader in question. This is why some individuals will enjoy substantial returns while others will inevitably falter. So, what approaches should be taken in order to mitigate the chances of incurring a fiscal loss?
[ymal]
Safe Investment Strategies to Adopt
Anyone who is contemplating an investment for business purposes should adopt a conservative approach. High-risk assets such as Forex pairs and initial public offerings (IPOs) are best to avoid, as losses can occur within a very short period of time. It is better to focus upon areas such as:
- Precious metals
- Commodities
- Blue-chip holdings
- Contracts for difference
- Bonds and treasuries
The main point to stress here is that longitudinal returns tend to be much more predictable when compared to short-term "punts". This is also the very same reason why some of the most successful online investors are always looking towards the horizon as opposed to remaining focused on any single trade.
Is online investing the right option for you? This is a very subjective question. The answer will normally involve how much liquidity you wish to obtain as well as the level of risk you are willing to accept at any given time. If performed correctly, such a strategy can offer up amazing results. However, always remember that the inherent dangers associated with any type of investment will need to be balanced with the potential rewards
A good credit score provides you with so many benefits, such as reasonable interest rates, faster loan approvals, and suitable insurance policies. Nearly 70 million Americans are suffering from bad credit because repairing your credit requires a lot of time and self-control. So, what is the best way to improve your credit score in no time? The answer is simple – buy a tradeline.
But, in order to understand how to improve your credit score by using a tradeline, you need to understand the term “tradeline” first.
What are tradelines?
A tradeline is basically any account appearing on your credit report. A tradeline keeps a record of creditor’s information to calculate his credit report. You can mutually benefit from someone with positive credit history and improve your credit score if he adds you as an authorized user (AU).
Most people ask their family and friends to add them as their AU, but if you want a quick improvement to your credit score, you can add users with exceptional credit history as an authorized user. These AU provide positive data regarding:
- Payment History
- Amount owed
- Length of history
Fair Isaac Corporation (FICO) places a credit score in 5 different grades.
- 720-850 Excellent
- 660-719 Good
- 620-659 Average
- 580-619 Below Average
- 350-579 Poor
Buying 2-3 seasoned tradeline can help you jump to a 720-850 credit score in a month.
What will a tradeline help you achieve?
A tradeline helps you improve your credit score so it will reap all the benefits a good credit score enables you to achieve. Without a good credit score, you will have limited access and services of your credit card, loan plan, and a higher rate of mortgages. In short, you will have to end up paying more money than usual.
But good tradelines on your account will help you achieve a credit score of 750 or higher in no time. When you buy an authorized tradeline from someone like Personal Tradelines, you are added as an AU to one of their credit card accounts, and it takes only 25-30 days to get your credit up to a good score.
Common mistakes people make when buying Tradelines
· Having no idea of how tradelines work
The most common mistake people do is buy a tradeline without having the slightest idea of how it works. I recommend that you read all about tradelines and their types before actually committing to buying one. You can also get help and information from tradelines vendors.
· Buying tradelines in hopes that it will unfreeze their accounts
Tradelines work by adding positive information to your account. If you have fraud alerts or credit freezes on your account, buying a tradeline will not work as new information can’t be posted on your credit report.
· Understanding the age factor of tradelines
The effectiveness of a tradeline is always going to be relative to how old your own account is and what is in your credit file. For example, if you have a 10-year-old account, an 8-year-old tradeline would not have much impact on it. However, if the account is only 1-2 years old, an 8-year-old tradeline would do wonders in increasing your credit score.
· Not having an idea of how credit score works
Before buying tradelines, it is vital to know how a credit score impacts your general lifestyle. Because even if you are successful at getting a good credit score after buying tradelines; you will have to follow a particular set of rules to maintain it.
· Going cheap
Some people go for 4-5 cheap tradelines instead of buying 2-3 seasoned tradelines. It ends up costing you more money, and you are better off buying seasoned or authorized tradelines rather than a lot of cheap tradelines.
Also, a cheap tradeline will not have that much positive effect on your credit report as they don’t have good age. This works against the goal of improving your credit score exponentially.
· Buying tradelines for shady companies
Unfortunately, there are a lot of companies that are selling tradelines, and it is tough to trust someone random. It is essential to do a background check on a company which includes customer reviews, their ratings, and some money-back guarantee to make that you are getting the best service possible.
Nigel Green, the chief executive of deVere Group, which has $12bn under advisement, is speaking out after Beijing announced on Friday it will impose new tariffs on $75 billion worth of US goods and resume duties on American autos.
The Chinese State Council said it will slap tariffs ranging from 5 to 10% in two batches. The first on 1 September and the second on 15 December.
Mr Green notes: “China and the US are playing a dangerous game of brinkmanship which will inevitably dent global growth at a time when the global economy is headed for a serious downturn.
“Both sides are getting hurt by the ongoing tit-for-tat trade war and given that they’re the world’s two largest economies its negative impact is far-reaching and intensifying. There’s some serious collateral damage.
“It is likely that there will be further retaliations in the form of tariffs, punitive sanctions on each other’s nation’s firms and, possibly, currency devaluations.”
He continues: “The already volatile markets have been rattled again by today’s news. Investors are getting spooked.
“However, the trade war will likely prove a blip for long-term investors.
“Indeed, investors should embrace some volatility as important buying opportunities.
“Fluctuations can cause panic-selling and mis-pricing. Sought-after stocks can then become cheaper, meaning investors can top up their portfolios and/or take advantage of lower entry points. This all typically results in better returns.
“A good fund manager will help investors seek out the opportunities that turbulence creates and mitigate potential risks as and when they are presented.
The deVere CEO concludes: “Many savvy investors will be using the fall-out of the US-China trade war to generate and build their wealth.”
The deadline to negotiate the exit was recently prolonged to October 31st, 2019. What are financial and economic consequences going to be for the UK? Public opinion has changed a lot lately. Theresa May has stepped down from the position of the UK’s Prime Minister and got replaced by Boris Johnson on 24th July. He promised that Brexit is going to be executed by 1st November with or without a deal with the European Union. Labour party demands another vote, as their members don’t think that leaving the EU would be a good idea at this moment.
Great Britain would no longer have the tariff-free trade status with other European countries if they decide to leave without a deal. This would have a significant increase in exports cost and automatically make the UK goods more expensive in Europe and potentially weaker the British Pound.
The prices to import goods to the UK would be higher, which also means some of them would simply reconsider distribution to Britain.
The same thing would happen with European merchants. The prices to import goods to the UK would be higher, which also means some of them would simply reconsider distribution to Britain. One-third of the food is coming from the European Union, which means inflation and a lower standard of living would be inevitable for UK residents. No deal agreement could also reignite the issues with North Ireland. This country would stay with the UK but there would be a custom border introduced between them and the Republic of Ireland. The last two things we would like to mention as a potential consequence of no-deal exit are rights for EU citizens living in the UK and outstanding bills. In case of an exit like this UK would have to pay $51 billion of debt and find a solution to guarantee rights to EU people within their borders.
Hard Brexit is the second alternative, and it is different in so many ways than the above-mentioned exit. This one would include a trade agreement with the EU; but this would require another re-schedule of the exit, as there is no enough time to negotiate it. Hard Brexit could have serious consequences on London as the financial centre. A lot of companies would stop using it as an English-speaking entry to the European Union economy. Also according to the latest research, more than six thousand people could lose jobs because of this and turn the real estate market into a disaster. There would be hundreds of office buildings in London sitting empty, without anyone to rent them. By comparing housing prices now and two years back, the price has already started to drop drastically. Another significant impact on UK companies would be the inability to place bids on public contracts in any European Union zone. This would take a massive toll on banking as well. Best betting sites experts have publish some odds that show that Hard Brexit deal would also increase costs of mobile phone services and airfares. Could the UK lose Scotland in case of Hard Brexit agreement? Potentially, yes. Scotland might have a bigger advantage of being an EU member, which also means a referendum to leave the United Kingdom. One of the most profitable industries in the UK is online gambling, and this one shouldn’t be affected much by any option.
Studies show that a large portion of forex traders fail. The problem is that most do not prepare adequately before starting their live trading activity.
You can increase your chances of becoming a successful trader by identifying the mistakes that most traders do and avoiding them. The following are some of the common mistakes that beginner forex traders do and our tips on how to avoid them.
Mistake 1: Not enough forex education
You will never trade successfully unless you invest in education. Many beginners start trading with a gambling mindset. However, successful forex trading requires an understanding of the global markets, trading strategies and technical and fundamental analysis. You need to know how to use financial information resources like Bloomberg or the Financial Times, charts and other tools.
Once you are confident with your knowledge you should test it with the help of the demo account. Demo trading is the best time to test different strategies. You should not start live trading until you identify a trading strategy that you feel comfortable with in the demo environment.
Mistake 2: No risk management plan
Forex trading is a high-risk venture, and it is therefore critical to have a risk management plan that factors in the amount of risk you are willing to take. Once you identify your risk appetite, you should identify trading tools to protect yourself against additional risk.
For example, you can implement a stop-loss to close trades when the prices hit your risk threshold. Likewise, you can have a 'take-profit' feature in place to lock in trades when your target price is reached. These are not the only risk management practices you can adopt and before you start trading you need to be aware of all important practices and how to use them to your advantage.
Mistake 3: not sticking to your risk management plan
You can have a trading strategy and a risk management plan, but you will achieve nothing unless you follow them. Remember that forex trading requires high discipline. Traders often ignore their risk plan when chasing losses or when they feel overconfident about a specific trade. You should learn to identify the urge to ignore your risk management plan as an emotional reaction and keep reminding yourself that emotions are the number one cause of wrong decision making in trading.
Mistake 4: Choosing the wrong broker
Most novice traders assume that all brokers are equal. This is not true. There are many factors that can differentiate one broker from the other and choosing the right broker has a huge impact on your success or failure in the trading world.
But if we can think of one factor that is simply crucial to check before choosing a broker it is the license. You should only work with forex brokers like Capex.com who have a license from top regulatory bodies. If a broker is not regulated by one of these bodies then it cannot be trusted and you should not work with them.
Bottom line
It is always good to learn from other people's mistakes and this is what we have tried to help you do in this article. We do hope that you learned the pits and falls of forex trading and that you will have the patience and discipline to avoid them.
Trading forex, especially with CFDs may involve a high risk and your potential losses when trading CFDs may be substantial.

